Bond market volatility: understanding the ups and downs

Anúncios
Bond market volatility refers to the fluctuations in bond prices driven by economic indicators, interest rates, and global events, impacting investor decisions and market stability.
Bond market volatility can feel like a roller coaster ride for investors. Have you ever wondered why bond prices fluctuate so much? In this article, we’ll dive into the factors behind these changes and their implications for your investments.
Anúncios
What causes bond market volatility?
Understanding bond market volatility is crucial for investors. It affects how bonds perform in response to varying economic conditions. Let’s explore some of the key factors that cause this volatility.
Anúncios
Economic Indicators
One major driver of bond market volatility is economic indicators. These indicators provide insights into the health of the economy. Examples include:
- Inflation rates
- Unemployment rates
- GDP growth
- Consumer sentiment
When these indicators change, they can cause significant fluctuations in bond prices.
Central Bank Policies
Another important factor is the actions of central banks. Decisions about interest rates can lead to volatility in the bond market. For instance, if a central bank raises interest rates, bond prices often fall. This inverse relationship can confuse many investors.
Additionally, the bond market reacts to monetary policy announcements. When interest rates are set to change, investors may sell or buy bonds quickly, leading to further volatility.
Market sentiment also plays a role in how bonds are traded. If investors feel uncertain about the future, they may sell off their bond holdings. This can create quick fluctuations in prices.
Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events can heavily influence bond market volatility. Wars, elections, and political unrest can cause confidence to waver. When investors feel uncertain, they may flee to safer assets, including bonds. This shift can lead to rapid movements in bond prices.
Ultimately, understanding these causes can help investors navigate the complexities of the bond market. By staying informed about economic indicators, central bank policies, and global events, they are better equipped to make sound investment choices.
Impact of economic indicators on bond prices
The relationship between economic indicators and bond prices is important for investors to understand. Economic indicators help gauge the health of the economy, and their impacts can be felt in the bond market.
Types of Economic Indicators
Different types of economic indicators can influence bond prices. These include:
- Leading Indicators: Predict future economic activity.
- Lagging Indicators: Reflect past economic performance.
- Coincident Indicators: Move with the economy’s current state.
When leading indicators show growth, bond prices may drop as investors anticipate rising interest rates.
Inflation Rates
Inflation is a significant factor that impacts bond prices. When inflation rises, it erodes the purchasing power of bond interest payments. This can lead to a sell-off in bonds, driving prices down. Conversely, low inflation often leads to higher bond prices as investors seek stable returns.
Moreover, central banks monitor inflation closely. Their decisions to raise or lower interest rates in response to inflation can further affect bond market volatility.
Employment Data
Employment data, such as unemployment rates and job growth figures, also influence investor sentiment. A strong job report may signal a robust economy, leading to concerns about inflation. This often results in falling bond prices as investors expect rate hikes to curb inflation.
In contrast, weak employment data typically leads to lower interest rates and increased bond demand. Investors often seek bonds as safe assets during economic uncertainty.
By staying informed about various economic indicators, investors can better anticipate shifts in bond prices. Understanding these connections helps in making informed investment decisions in a fluctuating market.
Strategies to navigate bond market fluctuations
Navigating bond market fluctuations can be challenging for investors. However, having effective strategies can help manage risks and seize opportunities. Here are some strategies to consider.
Diversification
Diversifying your bond portfolio is essential. By spreading investments across different types of bonds, you can reduce risk. Consider including:
- Treasury bonds: These are backed by the government and generally considered safe.
- CCorporate bonds: These may offer higher yields but come with higher risk.
- Muni bonds: Municipal bonds can provide tax benefits.
By having a variety of bonds, you can buffer against the impact of volatility in any single sector.
Monitoring Economic Indicators
Staying informed about economic indicators is key to navigating the bond market. Keep an eye on inflation rates, employment data, and central bank announcements. Understanding these factors can help you predict market movements.
For example, if inflation is expected to rise, you may want to consider reducing your exposure to long-term bonds. Conversely, in a low-inflation environment, it might be wise to invest in longer-dated bonds for better yields.
Interest Rate Strategies
Rates have a direct impact on bond prices. When interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall. To manage this, consider shortening the duration of your bond investments. Shorter-term bonds are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
Alternatively, if you believe rates will fall, investing in longer-term bonds can lock in higher yields. Understanding the interest rate cycle can guide your investment decisions effectively.
Using these strategies, you can better navigate bond market fluctuations and make informed decisions that align with your financial goals. Adapting to changing market conditions while staying diversified can help protect your investments.
Historical examples of bond volatility
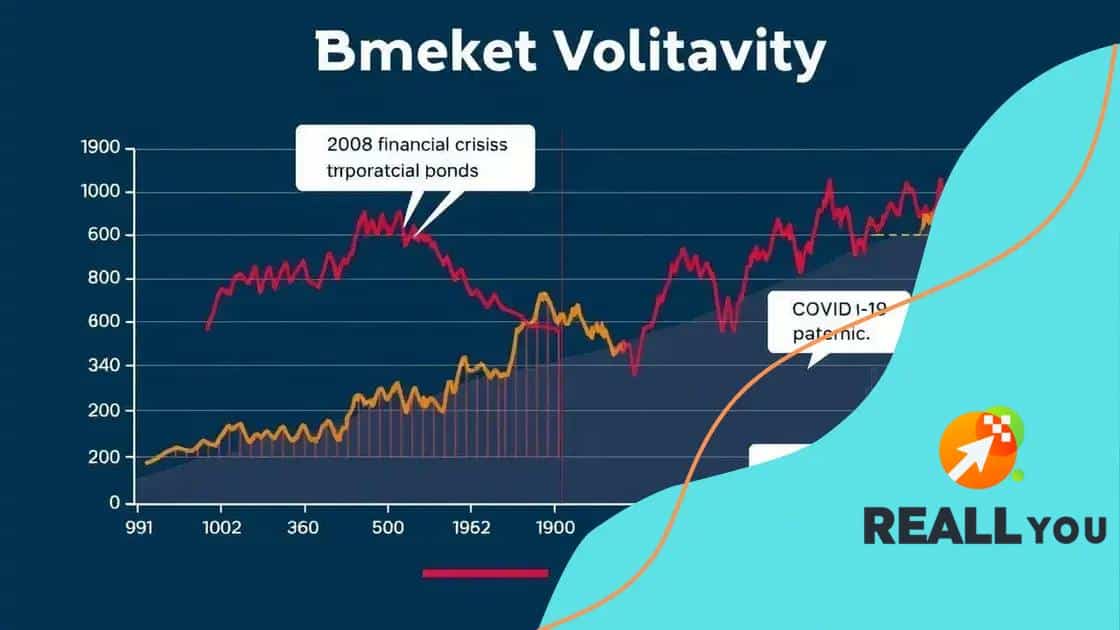
Examining historical examples of bond volatility can provide valuable lessons for investors. By understanding past events, investors can better predict future movements in the bond market.
The 2008 Financial Crisis
One significant example of bond volatility occurred during the 2008 financial crisis. As the crisis unfolded, investors panicked, leading to major sell-offs in various markets, including bonds. However, U.S. Treasury bonds became a safe haven. People flocked to these bonds, causing their prices to rise.
This event highlighted how economic instability can lead to heightened volatility in the bond market, impacting other securities as well.
COVID-19 Pandemic
Another notable example of bond market volatility came during the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in early 2020. Initially, there was a sharp drop in bond prices as investors feared widespread economic disruption. As uncertainty spread, the Federal Reserve stepped in to stabilize markets, which helped bond prices rebound.
Government intervention during periods of crisis generally can create volatility in bond prices. This event shows how swift reactions from central banks can influence market perceptions and lead to fluctuations.
1980s Inflation
Back in the late 1970s and early 1980s, high inflation caused significant turbulence in the bond markets. As inflation soared, interest rates followed suit, leading to falling bond prices. Investors re-evaluated their portfolios in response to these increasing rates.
This era is a prime example of how macroeconomic factors, like inflation, can drive bond market volatility. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for any investor.
By studying these historical instances, investors can develop a deeper understanding of how bond market volatility occurs and make more informed decisions during times of uncertainty.
Future trends in bond market volatility
The future of bond market volatility is influenced by several evolving trends that investors should be aware of. Understanding these trends can help investors make informed decisions moving forward.
Rising Interest Rates
One important trend is the potential for rising interest rates. Central banks might increase rates to combat inflation. As interest rates rise, bond prices typically fall. This inverse relationship could lead to increased volatility in the bond market.
Technological Advances
Another significant factor is the integration of technology in trading. Algorithmic trading and artificial intelligence are increasingly used for bond trading. These technologies can react to market changes rapidly, which may increase short-term volatility. While technology can enhance trading efficiency, it can also lead to sudden price movements.
Global Economic Interconnectedness
The global economy is more interconnected than ever. Events in one part of the world can quickly affect bond markets elsewhere. A crisis or economic slowdown in a major economy can trigger volatility in bonds. Investors should keep an eye on international developments and their potential impact on domestic markets.
Additionally, regulatory changes and fiscal policies can influence bond market stability. Changes in government spending or tax laws can sway investor confidence and lead to fluctuations in bond prices.
Investors should be proactive in understanding these trends. By staying informed and adapting strategies accordingly, they can manage risks and take advantage of opportunities presented by bond market volatility.
FAQ – Frequently Asked Questions about Bond Market Volatility
What is bond market volatility?
Bond market volatility refers to the fluctuations in bond prices due to changes in economic conditions, interest rates, and investor sentiment.
How do economic indicators affect bond prices?
Economic indicators like inflation and employment rates can influence investor expectations, leading to changes in bond prices and increased volatility.
What strategies can help manage bond market volatility?
Diversification, monitoring interest rates, and staying informed about economic trends are key strategies to help manage risks associated with bond market volatility.
Why is understanding historical examples of bond volatility important?
Studying historical examples helps investors recognize patterns and make informed decisions during periods of uncertainty in the bond market.







